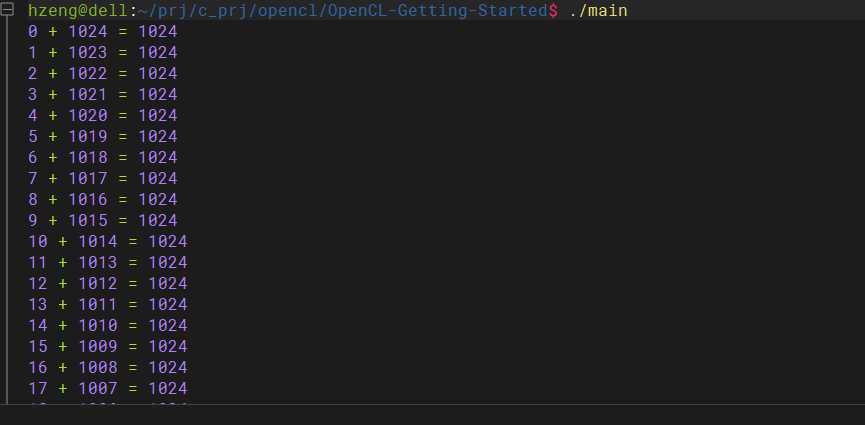
你的第一个openCL程序————向量加
介绍openCL程序编写流程,包括编译执行过程,以向量加为例,走完一个基本的流程,了解其过程。参考:https://www.eriksmistad.no/getting-started-with-opencl-and-gpu-computing/
openCL介绍
Open CL(开放计算语言)是一个新的框架,用于编写在不同供应商(AMD、Intel、ATI、Nvidia等)的不同计算设备(如CPU和GPU)上并行执行的程序。该框架定义了一种编写“内核”的语言。这些内核是在不同计算设备上运行的函数。在这篇文章中,我解释了如何开始使用Open CL,以及如何制作一个小型的Open CL程序,该程序将并行计算两个列表的总和。
以向量加为例,A和B是两个等长的向量,将其相加,得到向量C,如图1所示
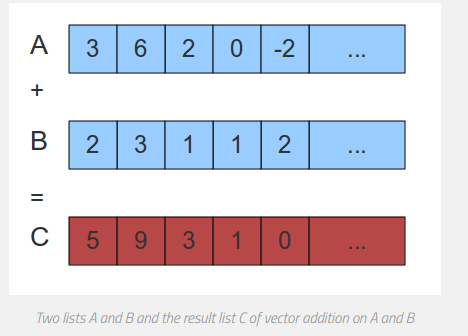
通常的做法是利用for循环遍历A,B两个向量,对每一个元素做相加,得到向量C的每一个元素。显然,这么做的时间复杂度是O(n),而实际上在该例子中,每一次迭代的计算都是各自不相关的,因此可以同时进行,并行以提高效率,如果有n个核,那并行起来时间复杂度就是O(1)。
为了使openCL完成以上过程,需要两部分代码:
- openCL内核代码:在计算设备上运行
- 主机(host)代码:在主机上运行,调用openCL代码执行
一、环境准备
以C程序为例(显然应该安装了gcc编译器),需包含openCL库,如果缺少该库(通常如果安装了cuda则会包含openCL库),在ubuntu上,可以通过包管理器直接安装:
sudo apt-get install ocl-icd-opencl-dev二、程序编写
如前文所述,openCL代码通常由openCL内核代码核主机代码组成,下面分别介绍二者,并给出完整示例代码及分析。
2.1 kernel编写
内核是用OpenCL语言编写的,它是C的一个子集,包含了许多数学和向量函数。执行向量加法运算的内核定义如下。文件命名为:vectorAddition.cl
__kernel void vector_add(__global const int *A, __global const int *B, __global int *C) {
// Get the index of the current element to be processed
int i = get_global_id(0);
// Do the operation
C[i] = A[i] + B[i];
}内核也有注释,基本和C语言一样,传入A,B,C数组指针,然后根据索引对对应位置相加得到向量C的结果。
2.2 主机程序编写
主机程序控制计算设备上内核的执行。主机程序是用C编写的,但存在用于C++和Python等其他语言的绑定。Open CL API是在CL.h(或apple的opencl.h)头文件中定义的。下面是在计算设备上执行上面内核的主机程序的代码。主机程序命名为:main.c ; 主要步骤如下:
2.2.1 OpenCL的编程步骤
- Discover and initialize the platforms
调用clGetPlatformIDs函数获取platform信息。 - Discover and initialize the devices
调用clGetDeviceIDs函数获取。并且可以简单修改参数,比如CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU换成CL_DEVICE_TYPE_CPU来更换openCL内核代码执行设备 - Create a context(调用clCreateContext函数)
上下文context可能会管理多个设备device。 - Create a command queue(调用clCreateCommandQueue函数)
一个设备device对应一个command queue。
上下文conetxt将命令发送到设备对应的command queue,设备就可以执行命令队列里的命令。 - Create device buffers(调用clCreateBuffer函数)
Buffer中保存的是数据对象,就是设备执行程序需要的数据保存在其中。
Buffer由上下文conetxt创建,这样上下文管理的多个设备就会共享Buffer中的数据。 - Write host data to device buffers(调用clEnqueueWriteBuffer函数)
- Create and compile the program
创建程序对象,程序对象就代表你的程序源文件或者二进制代码数据。 - Create the kernel(调用clCreateKernel函数)
根据你的程序对象,生成kernel对象,表示设备程序的入口。 - Set the kernel arguments(调用clSetKernelArg函数)
- Configure the work-item structure(设置worksize)
配置work-item的组织形式(维数,group组成等) - Enqueue the kernel for execution(调用clEnqueueNDRangeKernel函数)
将kernel对象,以及 work-item参数放入命令队列中进行执行。 - Read the output buffer back to the host(调用clEnqueueReadBuffer函数)
- Release OpenCL resources(至此结束整个运行过程)
下面是一些具体的对应本程序的步骤
- 获取有关平台和计算机上可用设备的信息(第42行)
- 选择要在执行中使用的设备(第43行)
- 创建Open CL上下文(第47行)
- 创建命令队列(第50行)
- 创建内存缓冲区对象(第53-58行)
- 将数据(列表A和B)传输到设备上的存储器缓冲区(线路61-64)
- 创建程序对象(第67行)
- 加载内核源代码(第24-35行)并对其进行编译(第71行)(在线执行)或加载预编译的二进制Open CL程序(离线执行)
- 创建内核对象(第74行)
- 设置内核参数(第77-79行)
- 执行内核(第84行)
- 读取内存对象。在这种情况下,我们从计算设备读取列表C(第88-90行)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#ifdef __APPLE__
#include <OpenCL/opencl.h>
#else
#include <CL/cl.h>
#endif
#define MAX_SOURCE_SIZE (0x100000)
int main(void) {
// Create the two input vectors
int i;
const int LIST_SIZE = 1024;
int *A = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*LIST_SIZE);
int *B = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*LIST_SIZE);
for(i = 0; i < LIST_SIZE; i++) {
A[i] = i;
B[i] = LIST_SIZE - i;
}
// Load the kernel source code into the array source_str
FILE *fp;
char *source_str;
size_t source_size;
fp = fopen("vector_add_kernel.cl", "r");
if (!fp) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to load kernel.\n");
exit(1);
}
source_str = (char*)malloc(MAX_SOURCE_SIZE);
source_size = fread( source_str, 1, MAX_SOURCE_SIZE, fp);
fclose( fp );
// Get platform and device information
cl_platform_id platform_id = NULL;
cl_device_id device_id = NULL;
cl_uint ret_num_devices;
cl_uint ret_num_platforms;
cl_int ret = clGetPlatformIDs(1, &platform_id, &ret_num_platforms);
ret = clGetDeviceIDs( platform_id, CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU, 1,
&device_id, &ret_num_devices);
// Create an OpenCL context
cl_context context = clCreateContext( NULL, 1, &device_id, NULL, NULL, &ret);
// Create a command queue
cl_command_queue command_queue = clCreateCommandQueue(context, device_id, 0, &ret);
// Create memory buffers on the device for each vector
cl_mem a_mem_obj = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY,
LIST_SIZE * sizeof(int), NULL, &ret);
cl_mem b_mem_obj = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY,
LIST_SIZE * sizeof(int), NULL, &ret);
cl_mem c_mem_obj = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_WRITE_ONLY,
LIST_SIZE * sizeof(int), NULL, &ret);
// Copy the lists A and B to their respective memory buffers
ret = clEnqueueWriteBuffer(command_queue, a_mem_obj, CL_TRUE, 0,
LIST_SIZE * sizeof(int), A, 0, NULL, NULL);
ret = clEnqueueWriteBuffer(command_queue, b_mem_obj, CL_TRUE, 0,
LIST_SIZE * sizeof(int), B, 0, NULL, NULL);
// Create a program from the kernel source
cl_program program = clCreateProgramWithSource(context, 1,
(const char **)&source_str, (const size_t *)&source_size, &ret);
// Build the program
ret = clBuildProgram(program, 1, &device_id, NULL, NULL, NULL);
// Create the OpenCL kernel
cl_kernel kernel = clCreateKernel(program, "vector_add", &ret);
// Set the arguments of the kernel
ret = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 0, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *)&a_mem_obj);
ret = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 1, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *)&b_mem_obj);
ret = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 2, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *)&c_mem_obj);
// Execute the OpenCL kernel on the list
size_t global_item_size = LIST_SIZE; // Process the entire lists
size_t local_item_size = 64; // Process in groups of 64
ret = clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(command_queue, kernel, 1, NULL,
&global_item_size, &local_item_size, 0, NULL, NULL);
// Read the memory buffer C on the device to the local variable C
int *C = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*LIST_SIZE);
ret = clEnqueueReadBuffer(command_queue, c_mem_obj, CL_TRUE, 0,
LIST_SIZE * sizeof(int), C, 0, NULL, NULL);
// Display the result to the screen
for(i = 0; i < LIST_SIZE; i++)
printf("%d + %d = %d\n", A[i], B[i], C[i]);
// Clean up
ret = clFlush(command_queue);
ret = clFinish(command_queue);
ret = clReleaseKernel(kernel);
ret = clReleaseProgram(program);
ret = clReleaseMemObject(a_mem_obj);
ret = clReleaseMemObject(b_mem_obj);
ret = clReleaseMemObject(c_mem_obj);
ret = clReleaseCommandQueue(command_queue);
ret = clReleaseContext(context);
free(A);
free(B);
free(C);
return 0;
}三、编译运行
如果Open CL头文件和库文件位于其适当的文件夹(/usr/include和/usr/lib)中,则以下命令将编译vector Addition程序。
gcc main.c -o vectorAddition -l OpenCL 运行结果如图2